Impact Orientation
The impact orientation analysis of the company’s sustainability targets is based on three assessment categories «transparency», «impact orientation» and «material topic». Read more about the methodology.
Industry Ranking
On average, all sectors score around 43% (36% in 2019). As in 2019, the food and beverage sector scores highest with 68% and the machine industry sector scoring lowest with 26%. The only sectors scoring above 50% – hence those classifying as ‘advancing’ sectors – are food & beverage and gastronomy & hospitality.
%
Average industry score
- Food & beverage sector (2019: 54%) 68%
- Gastronomy & Hospitality (2019: 30%) 54%
- Manufacturing industry (2019: 34%) 48%
- IT, medical & electrical engineering (2019: 27%) 48%
- Mobility, transport & logistics (2019: 29%) 47%
- Retail & wholesale trade (2019: 46%) 47%
- Construction builders & suppliers (2019: 40%) 45%
- Chemistry & pharmaceuticals (2019: 42%) 44%
- Insurance services (2019: 33%) 42%
- Financial services (2019: 30%) 40%
- Energy supply & distribution (2019: 30%) 36%
- Real estate (2019: 34%) 35%
- Other services (2019: 45%) 34%
- Machine industry (2019: 37%) 26%
Transparency
Reporting on achievements and downfalls (as for instance accidents, not-achieved targets). Whenever possible, negative or critical incidents should be mentioned, and the related causes, remedies and conse-quences should be discussed.
Impact orientation
Committing to short- as well as medium- and long-term targets that are SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic, Time-bound) and ideally impact-driven.
Material topics
Relating the company’s sustainability targets to material topics. Companies can gain credibility by showing a clear goal and way forward on areas that are material to the company and its stakeholders alike.
Transparency
A transparent disclosure of sustainability priorities includes not only positive disclosure, but also a negative or critical incidents, such as accidents, challenges or not-achieved targets. In those cases, the report should also disclose a response of the company explaining how it intends to overcome these issues.
Based on this set of criteria, 56% of the companies report at least somewhat or indeed balanced and transparently about their material issues. This is a significant increase compared to 2019, which recorded a 35% transparency level.

Impact
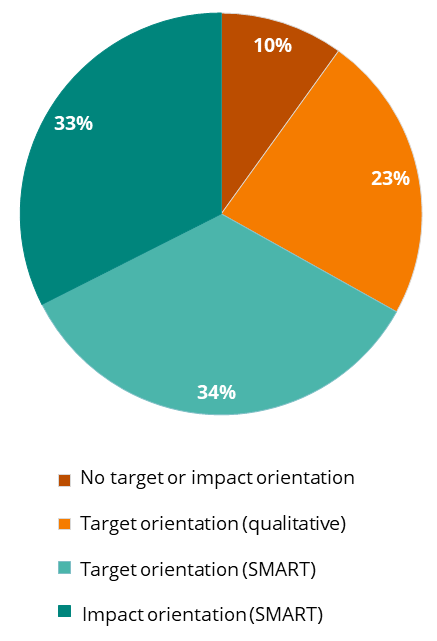
An impact-oriented disclosure of sustainability priorities includes a commitment to short- as well as medium- and long-term targets that are SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic, Time-bound) and impact-driven. The methodology concerning this criteria slightly changed from 2019 to 2021, hence the comparability to previous years is limited.
Two out of three targets set and disclosed in the reporting year 2020, are SMART or impact oriented targets.
Material Issues
Sustainability targets are most impactful, if they align with the material issues set by the company and its stakeholders. As for the category above, the methodology concerning this criteria slightly changed from 2019 to 2021, hence the comparability to previous years is limited.
78% of the sustainability targets set, are linked to material topics.